Probe Card PCB is A Significant Aspect of Semiconductor Wafer Test System
Keywords: probe card
In general, the probe card is considered disposable, and maintenance is essential to ensure its performance and usefulness. Overload and the deposition of debris from the wafer's binding material on the probe's tips or probe needles can cause resistance to increase and hinder correct readings.
What Does a Probe Card Indicate?
In essence, a probe card is a board or interface used to do wafer testing on semiconductor wafers. Before being manufactured and delivered, integrated circuits on the wafer are verified for electrical properties and performance via this link to the Automatic Test Equipment.
In essence, the probe card acts as a mechanical and electrical interface between the electronic test system and the equipment being tested. Each Probe Card comprises the following components:
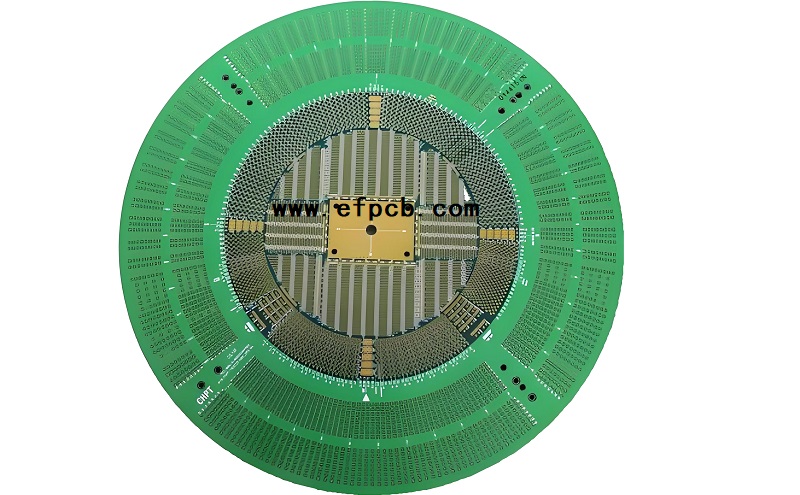
A probe card is a tool used to check silicon wafers during front-end LSI manufacture. A probe card is a circular printed circuit board (PCB) with connected probe pins or needles.
Each LSI chip, which is produced on a wafer, is electrically examined by simultaneously contacting several probe pin tips positioned on the PCB. Probe cards detect open and short circuits while also measuring electric current and high frequencies. A probe card is often attached to a wafer tester's prober and, during inspection, comes into contact with a wafer chip on a stage from above.
Examples of probe cards
Probe cards can be classed based on their structure, including probe alignment and fixation. Two example probe cards and their properties are presented below.
Vertical (advanced) probe card
A vertical (advanced) probe card consists of a PCB and a block on which perpendicular probes are placed. This sort of probe may be aligned in a grid or used to measure several chips. Maintenance is simple because the probes may be changed separately. Additionally, dents may be minimized, causing minimal harm to soldiers. However, the production costs are quite expensive, making it unsuitable for aluminum electrode pads on wafers.
Cantilever Probe Card
The needles on a cantilever probe card are composed of tungsten and other comparable materials. These needles are directly mounted on a PCB.
This kind may be created at a lesser cost than the vertical form. Its probes may also be positioned with narrower pitches to accommodate aluminum pads. When opposed to the vertical type, the cantilever type places more restrictions on pin placement and produces bigger dents. This kind also necessitates that operators devote time and effort to routine maintenance such as repair and adjustment.
The Printed Circuit Board
Organic substrate (multilayer)
We can also see that this Probe Card is now a component of a wafer test system, but it needs to be tested before being included in the test system. Due to increased power needs and device bandwidth, it is necessary to meet the requirement for high-performing power and signal transmission during electrical testing. These demands drive the problems associated with probe card testing.
The probe cards were designed to match all of the pads on the equipment being examined to the probes. To have a probe card created, the user must supply the manufacturer of the probe card PCBs with the mechanical designs for the device layout or a sample of the device.
Probe cards can be basic, with only one probe (a diode), or complex, with up to a thousand probes. The cable connection into that probe card (which may exceed 160 pins) is commonly made using an edge finger (up to 48 pins) and a ribbon cable.
How Do Probe Cards Work?
Consider the fabrication of semiconductors as an example of how to simplify the process. Throughout the silicon production process, several integrated circuits are found.
After that, the wafer is sliced, packed, and sent. However, the circuits' operation must be validated before packing. The probe card is used to assist with the electrical testing. This probe card is inserted into a prober, which is then attached to the tester, to provide an electrical channel between the tester and the semiconductor wafer. This probe card then connects to the IC chip pads on the wafer with its metallic needles or elements, transmitting the electrical data and essential test parameters.
Because the tester's head must be connected to the pads or metal bumps on that wafer to transfer electrical data, the prober might be thought of as such. This probe is used to dock the probe card, lower it to the wafer, and wait for the bumps or needles to make contact before allowing current to flow across the connections. Scrubbing away the layer of oxide and connecting to the metal beneath requires the movement of these probing needles as they come into contact with the metal bumps on the wafer.
Advanced Probe Types
The variety of probe card available today when deciding which sort of card to use to test the wafers demonstrates that probe technology has improved greatly in recent years. Let's look at the many sorts of advanced probes:
Vertical Probe
These vertical probes are cards used to examine multi-die devices, such as general-purpose microcomputers and logic. It is an excellent choice for high-frequency and tiny pad wafers since these needles are generally short and arranged vertically about the substrate.
MEMS-SP
This type of probe takes use of the benefits of MEMS technology while also allowing for very accurate and dependable testing of microprocessors and logic devices utilizing this probe card. The most advanced probe technology on the market is known as MEMS or Micro Electro Mechanical System. With only one landing, it can make one link to the wafer.
U-Probe cards are highly useful for testing memory devices. It can contact the wafer, which is around 12 inches long, with a single downward touch or contact.
It may be used anywhere, in any place on the semiconductor wafer, and it generates an even scrub to give the best results.
Why is Probe Card PCB Used?
The following are the most prevalent reasons why probe card PCBs are utilized. These include manipulator constraints, device layout, and manufacture. Now, let's go over each of them in depth.
Manipulator Limits
A typical prober could only place 8 to 12 manual manipulators around a platen aperture without using the probe card. Furthermore, the operator must manually adjust each probe tip, which is a time-consuming and labor-intensive operation.
Layout of the device
Probe cards are useful when a user needs to probe a device with a large number of pins (>12).
Production
Probing production applications make extensive use of probe cards. Production applications can range from as simple as a diode with one probe to as complex as integrated circuits with hundreds of probes.
This probe card may be electrically connected to the test instrument and physically docked with the prober. The primary purpose is to establish an electrical link between the test equipment and the wafer's circuits, enabling for validation and testing of these circuits before dicing and packing. It consists of a circuit board and several contact components, which are normally composed of metal but may be built of other materials. To help lower production costs and increase productivity, we design and manufacture a comprehensive range of high-performance probe cards.




