Challenges and Trends in PCB Manufacturing as well as Design
Keywords: PCB Fabrication, RF PCB
Thanks to emerging and new technologies that PCBs, the world of printed circuit boards is changing constantly. This is also due to the market for PCBs: Raw material supplies become more challenging to procure or dry up. Product development, PCB Fabrication, and design are reshaped by customer demands or Environmental changes.
Inscribed with conductive pathways, PCBs are other laminate material, composite epoxy, or thin plates of fiberglass that make it possible to connect components like integrated circuits, resistors, and transistors, so that data can be distributed as well as collected and functional networks can be established.
Introducing entirely new applications and methods, new functions and capabilities for PCBs emerge continuously. Predicting what patterns or trends will be most significant to PCB users is difficult as Information technology, the world of PCBs, and the science of computing change so much and so fast. It is also applicable to consumers, manufacturers, and other industries too. At the changes that are gaining a foothold, that has gained or have happened within the industry in a relatively short period, one has to look. To the future of the world of printed circuit boards, these are some of those accompanying challenges and trends that will be instrumental. They are:
Increasing high-power board demand
There’s a growing demand for high-power boards above 48 volts, thanks to many new solutions and technologies. Typically with solar energy applications, higher voltage levels are associated as in the range of 24 to 48 volts, most panels operate.
The option to accommodate more abundant and substantial components is one particular reason for increasing the power of PCBs. For instance, a system or device can operate longer with the help of Expensive battery packs. These are in high demand. The PCBs supporting such applications must be more powerful, efficient, and capable.
The issue
To unprecedentedly small sizes, RF PCB manufacturers must slim their products down. Yet, incredible amounts of heat can be produced by even lightweight and thin boards. Ultimately because of its components and how much more powerful a board has to be, thermal density and heat production has risen.
Even for high-power boards, heat dissipation and Thermal design must be optimized, which is a significant challenge to designers.
More PCBs for open communications and IoT
For virtually every industry, including the PCB sector, the Internet of things presents quite a fascinating challenge. On consumer-grade devices, this technology mainly focused on the past offering remote controls and monitoring through open-data connections. In commercial industries, IoT is much more prevalent today, such as development, retail, manufacturing, and much more although this is still the case.
They are generally portable and compact, which is the nature of IoT devices yet packed to the brim with functionality. So, many of which push the limits of what you can do with a lightweight PCB, they require substantial boards.
The design detail that requires security to be built-in as a foundational element is complicating things. That means more advanced forms of protection against tampering, printed circuit boards need to incorporate whereas formerly protecting the board and its components from environmental changes was the more significant concern.
Rather stringent regulations and standards have to be met by the IoT-ready PCBs, which govern their development directly. Despite their compact sizes, a lot more goes into the construction and design of PCBs for IoT-related technologies.
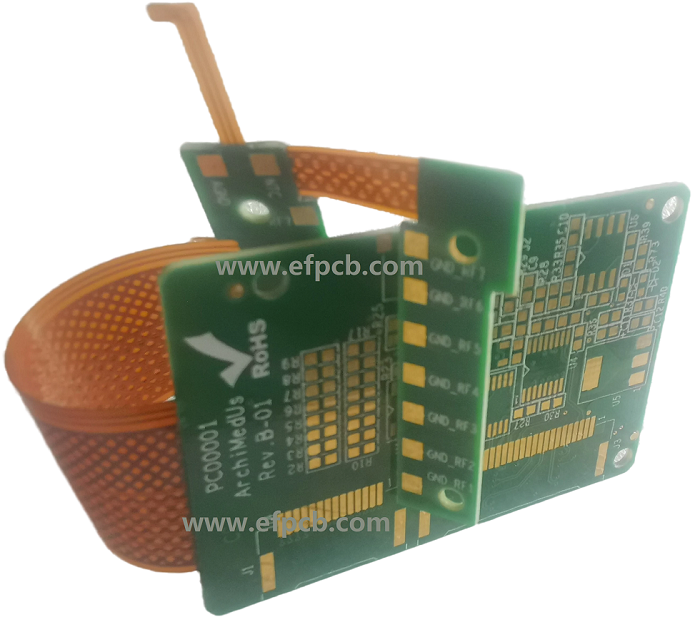
The rise of flex boards
Two design methods that used to be much rarer both rigid-flex boards and flex boards have recently risen in popularity for PCB manufacturing.
For more specific applications, including implants, medical devices, mobile consumer electronics, and sensors, Flexible circuits are ideal. For designs in which size, weight, and space limitations are quite strict, they are an excellent choice. For high-density and high-temperature applications, they’re also better suited.
On the other hand, Rigid-flex boards are a hybrid of flexible and rigid design methods. Features from both ends of the spectrum are exhibited by them, but may not match one or the other objective particularly well. In many cases, they become a sub-board. To either pure flexible or rigid boards, that that one is attached producing additional layers. However, multi-layer PCBs, with several steps included into the design phase, can be quite complex.
Functional benefits like maximum capability, smaller size, low weight, and higher reliability ratings are provided by both kinds. Also, because they are designed differently from traditional rigid boards, they offer a more extensive selection of material options for development.
Tighter controls of the supply chain
The hardware is a challenge as Cyber security is on nearly everyone’s mind these days. Especially as electronics become the go-to for critical systems in specific industries like manufacturing, counterfeit components are a growing problem for instance. More and more electronics are being called up by the digital revolution, all of which require attached components and PCBs.
Along with components, many innovative designs and novels will emerge, introducing new opportunities for counterfeiting and deception as boards themselves evolve. Boosting both visibility and accountability for all involved parties, the market will need to tighten its oversight of the supply chain.
To screen out potential applications for vulnerable or fake elements, new PCB manufacturing standards and methods must be developed in particular.
The COTS components spread
To commercial off-the-shelf components, and many PCB manufacturers are turning now aka COTS components. These are ready-made solutions that offer benefits of varying degrees apart from improving and speeding up the design process.
For critical and space-based systems, COTS is excellent news as third-party elements must meet regulatory guidelines and stringent standardization. With much lower overhead, A higher degree of efficiency and reliability can be achieved.
As it portends a much-reduced need to vet them, some PCB experts worry that rampant commercialization of design could mean less regulation of components: If everyone knows they are produced to higher quality standards and they’re receiving PCB products from a reputable source, there will be an assumption that regulation will be minimized.
New PCB production standards
The coming changes in PCB manufacturing and design are signified by these trends, and some are likely to be more disruptive to the current market than others. But in terms of performance planning and design innovation, they also show positive forward momentum.
In response to more commercial standards and unified regulations as well as regarding product reliability and design, the PCB industry along with PCB Fabrication as a whole is evolving and improving. For the world of printed circuit boards, this is a period of innovation.




